*We are a reader-supported website. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn a small affiliate commission at no extra cost to you. Home Media Entertainment does not accept money for reviews.*
TV technology has always been a battleground of fierce competition. Manufacturers are constantly competing to surpass each other in the quest for more powerful displays that captivate viewers with every pixel.
As a result, over the past decade, television technology has experienced many groundbreaking improvements. Some of them include the introduction of 8K and 4K resolution, micro-LED and mini-LED displays, OLED and QLED panels, Dolby Atmos surround sound, and High Dynamic Range (HDR) video.
These remarkable developments since 2012 have compelled consumers to shift their
perspectives and embrace the latest TV technology to watch not only their favorite shows and movies. But also play a wide variety of games including single player offline games, multiplayer online games and a wide variety of other types like roulette online games.
This article explores the latest TV innovations that have revolutionized the television
industry until today.
QD-OLED Panel Technology
At first glance, QD-OLED may appear to be a straightforward concept – combining quantum dots with OLED. However, if you carefully look at its design, it is a rather interesting and honestly impressive concept.
Quantum dots improve the illumination of LED backlights in QLED TVs. The
light is then managed by a color filter that separates the illumination into blue, green, and red subpixels. In the case of QD-OLED, quantum dots serve as subpixels themselves.
This means that the green and red light they emit must function independently, with the blue OLED light activating them. As a result, the quantum dots account for most of the imagery visible on a QD-OLED screen.
The image produced by QD-OLED technology is truly remarkable! It surpasses the
capabilities of both QLED and OLED technology by expanding the color gamut and
enhancing color brightness to a degree neither QLED nor OLED could ever achieve.
This technology combines the deep black levels of OLED with the remarkable brightness levels associated with QLED TVs, offering us the ultimate fusion of both worlds.
Unsurprisingly, QD-OLED TVs such as the A95K and S95B are universally acclaimed as the pinnacle of television excellence. At least up to the point of their release.
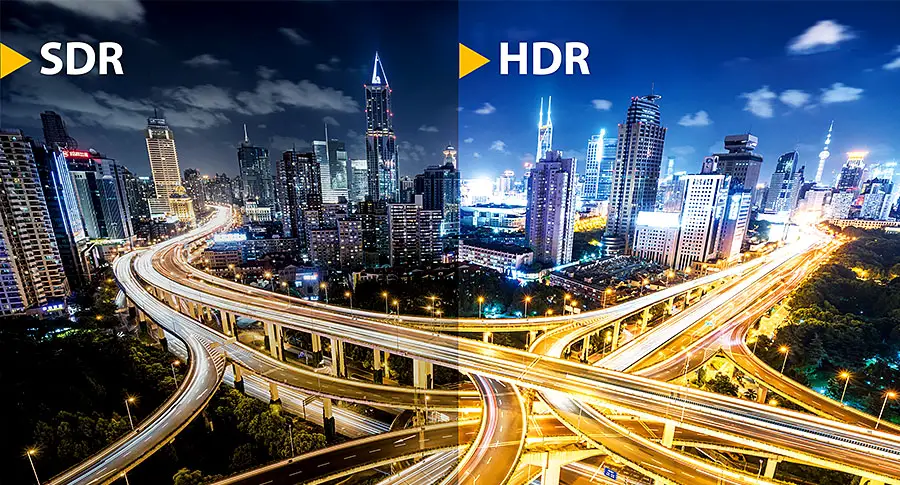

High Dynamic Range (HDR)
High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology was introduced a few years back and revolutionized the display experience by expanding color range, brightness levels, and contrast in images and videos.
By enriching the quality of TV pictures, HDR elevates visual immersion and realism. It
accomplishes this by enhancing brightness, intensifying dark shades, and amplifying vibrant colors.
With increased contrast ratios, HDR adds more visual detail not possible with SDR content. It brings deep blacks, radiant whites, and a wide spectrum of vivid colors to life on-screen.
HDR also comes in different formats like Dolby Vision, HDR10, HDR10+ and HLG. The format selection depends on your desired content and your TV’s capabilities. Unfortunately the HDR format war is a fact that we cannot ignore and each one of the big three (Samsung, LG, Sony) seem determined to stick to specific sides. Which in the end hurts the end consumer more than anyone else.
Micro-LED and Mini-LED Displays
Micro-LED and mini-LED displays are advanced TV technologies that were created to enhance visual performance. This happened due to the various weaknesses in traditional LED LCD technologies.
Micro-LED displays appeared some years ago but still haven’t gain any meaningful traction. These use self-emissive LED modules as pixels, offering precise control over brightness and color. As a result you get exceptional contrast, vibrant colors, and deep blacks. They also provide high peak brightness, wide viewing angles, and fast response times.
On the other hand Mini-LED became widely available very fast replacing aging FALD backlight TVs. These displays utilize miniaturized LEDs as a backlighting system. This allows for precise local dimming and backlight control.
By using thousands of dimming zones, they enhance contrast, black levels and minimize blooming. But obviously their performance depends on a lot of factors including the number of dimming zones included. But the fact is that both technologies deliver superior picture quality and HDR performance than what was previously achievable.
Although currently both technologies are mostly common in high-end displays, due to manufacturing costs, wider micro LED adoption is still far away. These displays have the potential to be used in various consumer electronic devices.
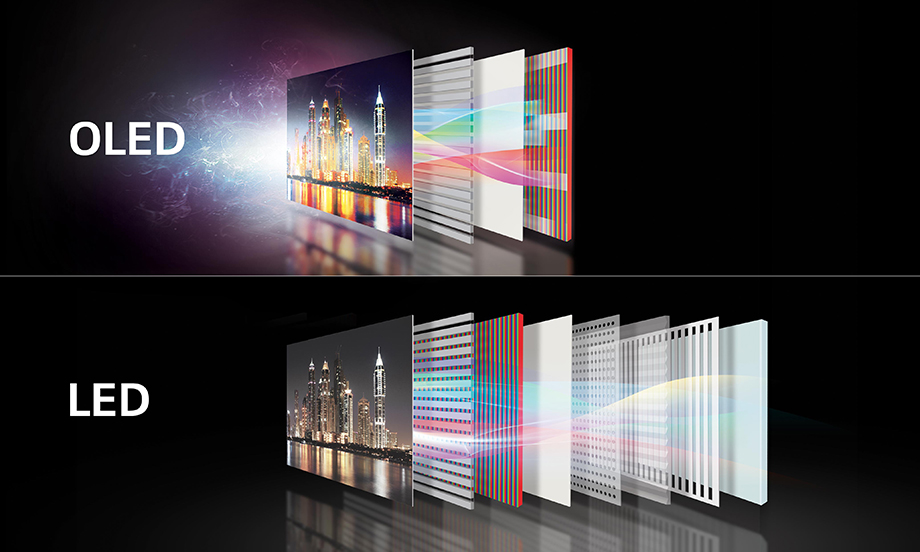

OLED and QLED Panels
Let’s talk next about OLED and QLED. OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) and QLED (Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diode) panels are display technologies renowned for their visual prowess. Both of them are available in TVs for a few good years now and each one has its own strengths and weaknesses.
On the one hand OLED panels feature self-emissive pixels that deliver perfect blacks, infinite contrast, and vibrant colors. They offer wide viewing angles and fast response times for immersive experiences.
QLED panels, on the other hand, utilize quantum dots to emit precise colors when excited by a backlight. QLED displays excel in color accuracy, high peak brightness, and wide color gamut, making them ideal for vibrant visuals and HDR content in bright environments.
Each technology has its strengths: OLED boasts superior contrast and viewing angles, while QLED stands out in color accuracy and brightness. The choice between the two depends on personal preferences and specific requirements. But between the two, most consider OLED the superior one. And this because of the true deep blacks OLED technology can achieve. Some that is almost impossible for a non OLED panel to have.
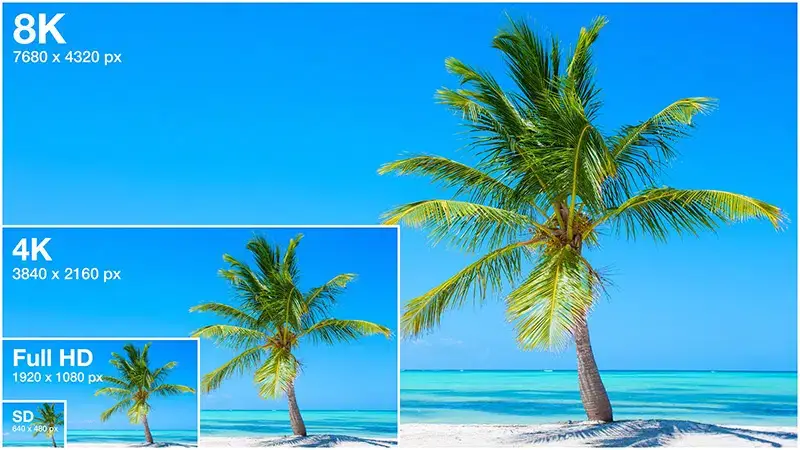

8K and 4K Resolutions
8K and 4K resolutions represent different levels of visual detail on display screens.
With 8K resolution you get incredibly high level of detail with 7680 x 4320 pixels. Thus you get four times the pixel density of 4K and 16 times that of Full HD. It delivers exceptionally sharp and lifelike images, ideal for large screens and professional applications.
Likewise 4K resolution, with 3840 x 2160 pixels, provides four times the pixel density of Full HD, delivering sharp images with vibrant colors. It has gained popularity in consumer displays, offering an immersive viewing experience with excellent clarity and detail.
The choice between 8K and 4K depends on many factors. Some of them are screen size, viewing distance, availability of 8K content, and budget. While 8K provides ultimate detail, 4K remains widely adopted, balancing visual quality and affordability. Unfortunately 8K resolution failed to gain any meaningful traction. And this comes down to a single factor. Almost no commercial released 8K content.

Dolby Atmos
But it’s not only picture where manufacturers try to push the envelope. It is with sound also, and here we find Dolby Atmos. Dolby Atmos is an advanced surround sound technology that creates a three-dimensional audio experience. But unlike traditional channel based systems, it uses object-based audio, allowing precise positioning and movement of sounds in a 3D space, including overhead.
This immersive technology enhances localization and creates a realistic sense of depth and movement, unlike anything that could be achieved before. Dolby Atmos is compatible with a wide range of speaker setups, enhancing the audio quality across movies, TV shows, games, and music.
By delivering a truly immersive and lifelike soundstage, this advanced technology delivers a cinematic experience where sounds originate from every direction. This includes not only ear level sounds but also overhead ones. The result is a profound immersion, as the audio envelops the listener and brings the content to life.
For more sponsored articles you can check our dedicated Sponsored Articles section.
